

How Do We Achieve Excellence in Quality and Operational Efficiency?
In response to global sustainability policies, Chung Hwa Pulp has proactively implemented a wide range of cleaner production initiatives and continuous improvement programs. We are committed to enhancing the efficiency of water, air, and energy resource use. In parallel, we have obtained various management system certifications to support continuous improvement and risk management across our operations, covering quality, environment, energy, occupational safety, and raw material traceability. Through these integrated management practices, we sustain operational growth while strengthening long-term resilience.
Chung Hwa Pulp has established a Greenhouse Gas Reduction Task Force to systematically identify and inventory on-site emission sources, develop mitigation measures, and oversee implementation. Inventory results are reported to the national greenhouse gas registry and disclosed in our Sustainability Report.
As of 2024, compared to the 2018 baseline year, emissions have already been reduced by 10,000 tons, achieving a 9.8% reduction, thus meeting the 2025 target ahead of schedule.
Total greenhouse gas emissions in 2024: 920,732 metric tons CO₂e
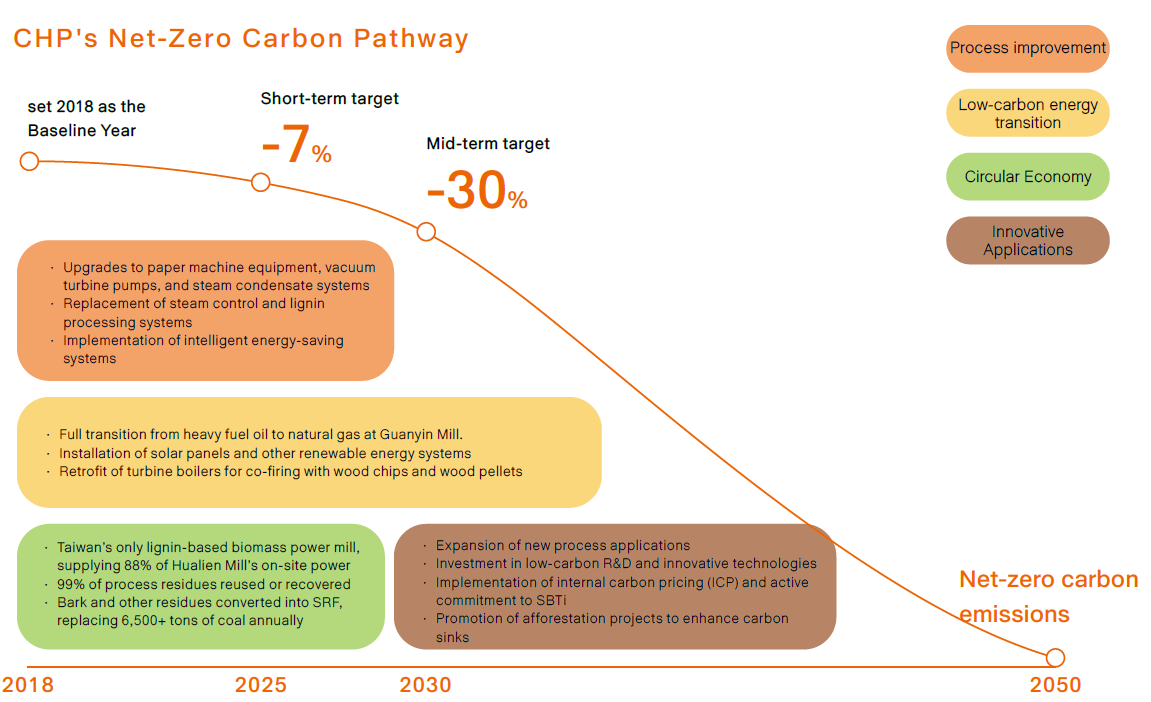 Sustainability Roadmap
Sustainability Roadmap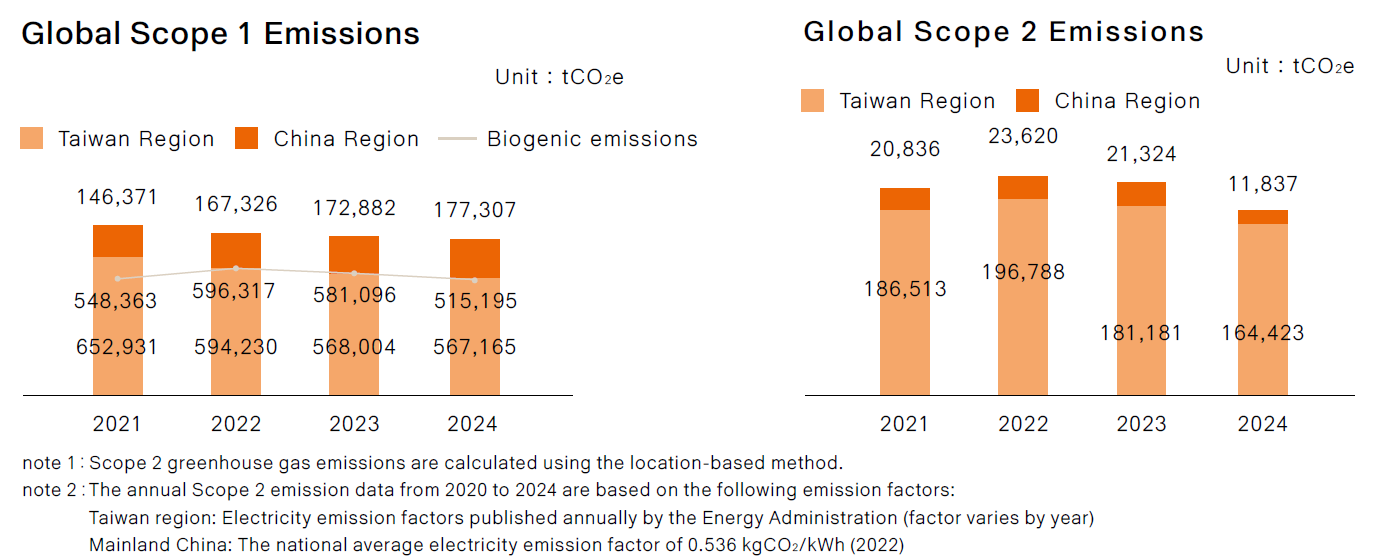

Water Resource Management
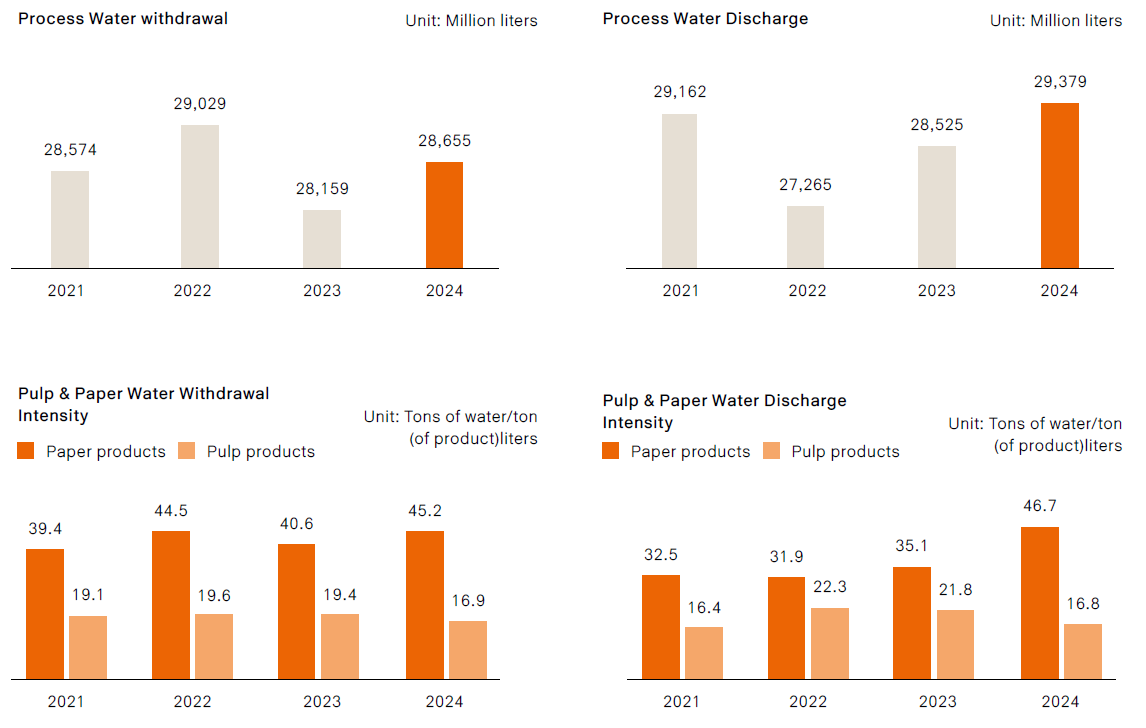
Following a peak in total process water withdrawal in 2022 (29,029 million liters), usage declined significantly in 2023 and rebounded slightly to 28,655 million liters in 2024, remaining below 2021–2022 levels. This trend demonstrates the effectiveness of water management and conservation initiatives.
Total process wastewater discharge in 2024 reached 29,379 million liters, primarily due to the inflow of agricultural irrigation drainage (averaging approximately 5.8 million liters per day) from nearby farmland into certain production sites, which is subsequently discharged through the plant outfall. In accordance with the Regulations Governing Water Pollution Control Measures and Test Reporting, effluent flow meters must be installed at the terminal discharge outlet, resulting in recorded discharge volumes exceeding process water withdrawal.
In terms of water intensity: Pulp products: Water intensity decreased in 2023 but increased to 45.2 tons of water per ton of product in 2024.
Paper products: Water intensity has shown a long-term downward trend, reaching 16.9 tons of water per ton of product in 2024, reflecting stable improvements in water efficiency.
Regarding effluent intensity: Pulp products: Effluent intensity reached 46.7 tons per ton of product in 2024, indicating the need for continued focus on water reuse and discharge management
Paper products: Effluent intensity remained stable at 16.8 tons per ton of product, consistent with improvements in water-use efficiency.
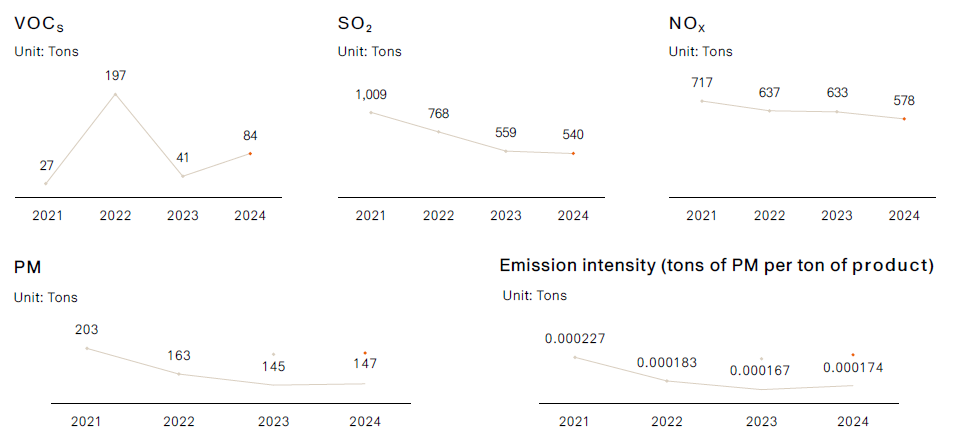
Chung Hwa Pulp’s air quality management complies fully with regulatory requirements while continuously evaluating and upgrading pollution control technologies. The Company does not emit hazardous air pollutants.
In recent years, aging equipment has been replaced, contributing not only to carbon reduction but also to improved air quality. Compared with the 2021 baseline, total emissions in 2024 show declining trends:
Data source: Aggregated values from real-time monitoring using on-site flow meters.
In addition, Chung Hwa Pulp’s Hualien Mill has received guidance from the county government to install perimeter hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) detectors and implement intelligent inspection systems. We have also invited domestic experts and scholars specializing in air pollution control to conduct on-site assessments, identify odor sources within production processes, and propose effective mitigation strategies to address odor-related concerns.
*Source: Cumulative values based on real-time monitoring from in-mill flow meters.

In addition, Chung Hwa Pulp’s Hualien Mill has received guidance from the county government to install perimeter hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) detectors and implement intelligent inspection systems. We have also invited domestic experts and scholars specializing in air pollution control to conduct on-site assessments, identify odor sources within production processes, and propose effective mitigation strategies to address odor-related concerns.
Resource Reuse
How Do We Achieve Excellence in Quality and Operational Efficiency?
NOx: 19% reduction
SO₂: 47% reduction
Particulate matter: 28% reduction
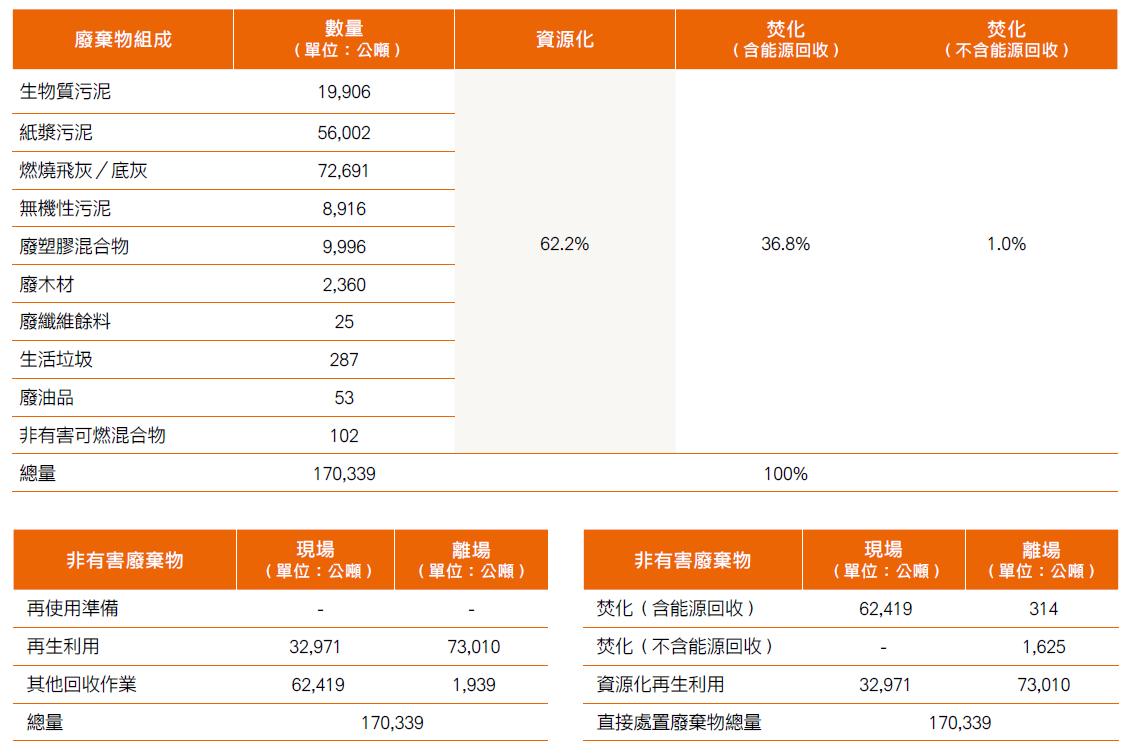
Most by-products generated during our production processes possess fibrous characteristics and are classified as non-hazardous waste. Based on treatment methods, they are categorized into:
Our operations prioritize on-site recycling and waste-to-energy solutions, with 99% of by-products either recycled or incinerated with energy recovery. Combustible, high-calorific residues are used as alternative fuels, while sludge is recycled through composting or transformed into innovative products. Off-site by-products are partially reused as raw materials for cement production.
To ensure full traceability and proper handling of waste streams, Chung Hwa Pulp carefully selects waste collection, treatment, and recycling contractors, continuously strengthening audits, monitoring, and management processes.
Material recycling and reuse
Incineration with energy recovery
Incineration without energy recovery
Today’s Waste Is Tomorrow’s Treasure
We continuously seek new ways to maximize resource circulation and extend the number of reuse cycles.
Wood sourced from forests is a vital natural resource upon which Chung Hwa Pulp depends. By extending the life cycle of trees and supporting sustainable forest management, we can ensure long-term, stable resource supply. Most by-products generated during paper manufacturing can be recycled and reused. Organic-rich residues, which account for the largest proportion, are returned to the land to provide nutrients.
Beyond this, we actively apply innovative technologies and recycling approaches to give waste materials new value and renewed life.


Natural compost


Building materials

Cement products


RDF fuel
We are committed to continuously extending the life cycle of paper by building a circular supply chain, making our paper products more environmentally sustainable.